OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
Aktualisiert Z-Score Weighted Trend System I [InvestorUnknown]
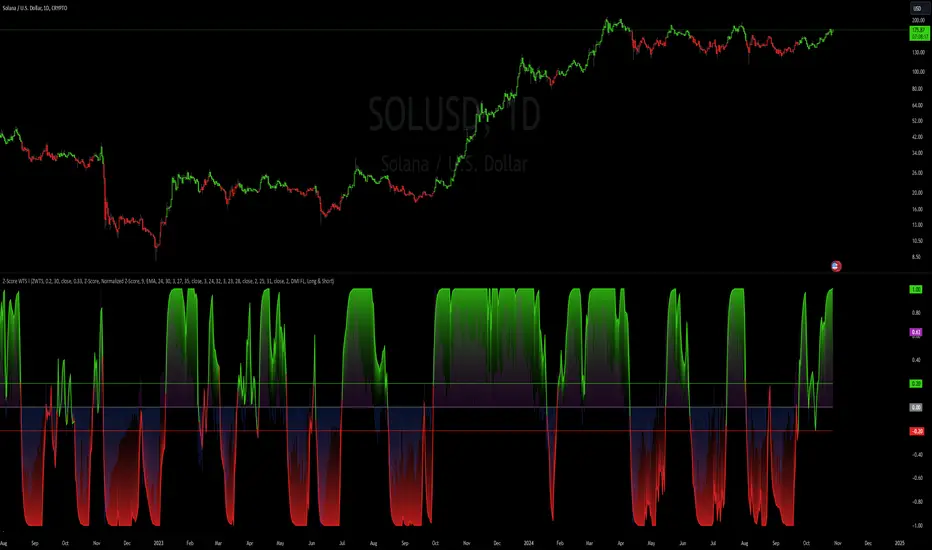
The Z-Score Weighted Trend System I is an advanced and experimental trading indicator designed to utilize a combination of slow and fast indicators for a comprehensive analysis of market trends. The system is designed to identify stable trends using slower indicators while capturing rapid market shifts through dynamically weighted fast indicators. The core of this indicator is the dynamic weighting mechanism that utilizes the Z-score of price, allowing the system to respond effectively to significant market movements.
Dynamic Z-Score-Based Weighting System
Pine Script®
Choice of Z-Score Normalization
Traders have the flexibility to select different Z-score processing methods to better suit their trading preferences:
Pine Script®

Slow and Fast Indicators
The indicator uses a combination of slow and fast indicators:
Each indicator is calculated using for-loop methods to provide a smoothed and averaged view of price data over varying lengths, ensuring stability for slow indicators and responsiveness for fast indicators.
Signal Calculation
The final trading signal is determined by a weighted combination of both slow and fast indicators. The slow indicators provide a stable view of the trend, while the fast indicators offer agile responses to rapid market movements. The signal calculation takes into account the dynamic weighting of fast indicators based on the Z-score:
Pine Script®
Backtest Mode and Performance Metrics
The indicator features a detailed backtesting mode, allowing traders to compare the effectiveness of their selected settings against a traditional Buy & Hold strategy. The backtesting provides:
Pine Script®

Calibration Mode
A Calibration Mode is included for traders to focus on individual indicators, helping them fine-tune their settings without the influence of other components. In Calibration Mode, the user can visualize each indicator separately, making it easier to adjust parameters.
Alerts
The indicator includes alerts for long and short signals when the indicator changes direction, allowing traders to set automated notifications for key market events.
Pine Script®
Important Note:
Dynamic Z-Score-Based Weighting System
- The Z-Score Weighted Trend System I utilizes the Z-score of price to assign weights dynamically to fast indicators. This mechanism is designed to capture rapid market shifts at potential turning points, providing timely entry and exit signals.
- Traders can choose from two primary weighting mechanisms:
- Threshold-Based Weighting: The fast indicators are given weight only when the absolute Z-score exceeds a user-defined threshold. Below this threshold, fast indicators have no impact on the final signal.
- Continuous Weighting: By setting the threshold to zero, fast indicators always contribute to the final signal, regardless of Z-score levels. However, this increases the likelihood of false signals during ranging or low-volatility markets
// Calculate weight for Fast Indicators based on Z-Score (Slow Indicator weight is kept to 1 for simplicity)
f_zscore_weights(series float z, simple float weight_thre) =>
float fast_weight = na
float slow_weight = na
if weight_thre > 0
if math.abs(z) <= weight_thre
fast_weight := 0
slow_weight := 1
else
fast_weight := 0 + math.sqrt(math.abs(z))
slow_weight := 1
else
fast_weight := 0 + math.sqrt(math.abs(z))
slow_weight := 1
[fast_weight, slow_weight]
Choice of Z-Score Normalization
Traders have the flexibility to select different Z-score processing methods to better suit their trading preferences:
- Raw Z-Score or Moving Average: Traders can opt for either the raw Z-score or a moving average of the Z-score to smooth out fluctuations.
- Normalized Z-Score (ranging from -1 to 1) or Z-Score Percentile: The normalized Z-score is simply the raw Z-score divided by 3, while the Z-score percentile utilizes a normal distribution for transformation.
f_zscore_perc(series float zscore_src, simple int zscore_len, simple string zscore_a, simple string zscore_b, simple string ma_type, simple int ma_len) =>
z = (zscore_src - ta.sma(zscore_src, zscore_len)) / ta.stdev(zscore_src, zscore_len)
zscore = switch zscore_a
"Z-Score" => z
"Z-Score MA" => ma_type == "EMA" ? (ta.ema(z, ma_len)) : (ta.sma(z, ma_len))
output = switch zscore_b
"Normalized Z-Score" => (zscore / 3) > 1 ? 1 : (zscore / 3) < -1 ? -1 : (zscore / 3)
"Z-Score Percentile" => (f_percentileFromZScore(zscore) - 0.5) * 2
output
Slow and Fast Indicators
The indicator uses a combination of slow and fast indicators:
- Slow Indicators (constant weight) for stable trend identification: DMI (Directional Movement Index), CCI (Commodity Channel Index), Aroon
- Fast Indicators (dynamic weight) to identify rapid trend shifts: ZLEMA (Zero-Lag Exponential Moving Average), IIRF (Infinite Impulse Response Filter)
Each indicator is calculated using for-loop methods to provide a smoothed and averaged view of price data over varying lengths, ensuring stability for slow indicators and responsiveness for fast indicators.
Signal Calculation
The final trading signal is determined by a weighted combination of both slow and fast indicators. The slow indicators provide a stable view of the trend, while the fast indicators offer agile responses to rapid market movements. The signal calculation takes into account the dynamic weighting of fast indicators based on the Z-score:
// Calculate Signal (as weighted average)
float sig = math.round(((DMI*slow_w) + (CCI*slow_w) + (Aroon*slow_w) + (ZLEMA*fast_w) + (IIRF*fast_w)) / (3*slow_w + 2*fast_w), 2)
Backtest Mode and Performance Metrics
The indicator features a detailed backtesting mode, allowing traders to compare the effectiveness of their selected settings against a traditional Buy & Hold strategy. The backtesting provides:
- Equity calculation based on signals generated by the indicator.
- Performance metrics comparing Buy & Hold metrics with the system’s signals, including: Mean, positive, and negative return percentages, Standard deviations, Sharpe, Sortino, and Omega Ratios
// Calculate Performance Metrics
f_PerformanceMetrics(series float base, int Lookback, simple float startDate, bool Annualize = true) =>
// Initialize variables for positive and negative returns
pos_sum = 0.0
neg_sum = 0.0
pos_count = 0
neg_count = 0
returns_sum = 0.0
returns_squared_sum = 0.0
pos_returns_squared_sum = 0.0
neg_returns_squared_sum = 0.0
// Loop through the past 'Lookback' bars to calculate sums and counts
if (time >= startDate)
for i = 0 to Lookback - 1
r = (base - base[i + 1]) / base[i + 1]
returns_sum += r
returns_squared_sum += r * r
if r > 0
pos_sum += r
pos_count += 1
pos_returns_squared_sum += r * r
if r < 0
neg_sum += r
neg_count += 1
neg_returns_squared_sum += r * r
float [] export_array = array.new_float(12)
// Calculate means
mean_all = math.round((returns_sum / Lookback), 4)
mean_pos = math.round((pos_count != 0 ? pos_sum / pos_count : na), 4)
mean_neg = math.round((neg_count != 0 ? neg_sum / neg_count : na), 4)
// Calculate standard deviations
stddev_all = math.round((math.sqrt((returns_squared_sum - (returns_sum * returns_sum) / Lookback) / Lookback)) * 100, 2)
stddev_pos = math.round((pos_count != 0 ? math.sqrt((pos_returns_squared_sum - (pos_sum * pos_sum) / pos_count) / pos_count) : na) * 100, 2)
stddev_neg = math.round((neg_count != 0 ? math.sqrt((neg_returns_squared_sum - (neg_sum * neg_sum) / neg_count) / neg_count) : na) * 100, 2)
// Calculate probabilities
prob_pos = math.round((pos_count / Lookback) * 100, 2)
prob_neg = math.round((neg_count / Lookback) * 100, 2)
prob_neu = math.round(((Lookback - pos_count - neg_count) / Lookback) * 100, 2)
// Calculate ratios
sharpe_ratio = math.round((mean_all / stddev_all * (Annualize ? math.sqrt(Lookback) : 1))* 100, 2)
sortino_ratio = math.round((mean_all / stddev_neg * (Annualize ? math.sqrt(Lookback) : 1))* 100, 2)
omega_ratio = math.round(pos_sum / math.abs(neg_sum), 2)
// Set values in the array
array.set(export_array, 0, mean_all), array.set(export_array, 1, mean_pos), array.set(export_array, 2, mean_neg),
array.set(export_array, 3, stddev_all), array.set(export_array, 4, stddev_pos), array.set(export_array, 5, stddev_neg),
array.set(export_array, 6, prob_pos), array.set(export_array, 7, prob_neu), array.set(export_array, 8, prob_neg),
array.set(export_array, 9, sharpe_ratio), array.set(export_array, 10, sortino_ratio), array.set(export_array, 11, omega_ratio)
// Export the array
export_array
//}
Calibration Mode
A Calibration Mode is included for traders to focus on individual indicators, helping them fine-tune their settings without the influence of other components. In Calibration Mode, the user can visualize each indicator separately, making it easier to adjust parameters.
Alerts
The indicator includes alerts for long and short signals when the indicator changes direction, allowing traders to set automated notifications for key market events.
// Alert Conditions
alertcondition(long_alert, "LONG (Z-Score Weighted Trend System)", "Z-Score Weighted Trend System flipped ⬆LONG⬆")
alertcondition(short_alert, "SHORT (Z-Score Weighted Trend System)", "Z-Score Weighted Trend System flipped ⬇Short⬇")
Important Note:
- The default settings of this indicator are not optimized for any particular market condition. They are generic starting points for experimentation. Traders are encouraged to use the calibration tools and backtesting features to adjust the system to their specific trading needs.
- The results generated from the backtest are purely historical and are not indicative of future results. Market conditions can change, and the performance of this system may differ under different circumstances. Traders and investors should exercise caution and conduct their own research before using this indicator for any trading decisions.
Versionshinweise
Updated the code to pinescript v6, added backtesting library v2 with more backtesting functions and removed old backtesting functions from the codeOpen-source Skript
Ganz im Sinne von TradingView hat dieser Autor sein/ihr Script als Open-Source veröffentlicht. Auf diese Weise können nun auch andere Trader das Script rezensieren und die Funktionalität überprüfen. Vielen Dank an den Autor! Sie können das Script kostenlos verwenden, aber eine Wiederveröffentlichung des Codes unterliegt unseren Hausregeln.
Haftungsausschluss
Die Informationen und Veröffentlichungen sind nicht als Finanz-, Anlage-, Handels- oder andere Arten von Ratschlägen oder Empfehlungen gedacht, die von TradingView bereitgestellt oder gebilligt werden, und stellen diese nicht dar. Lesen Sie mehr in den Nutzungsbedingungen.
Open-source Skript
Ganz im Sinne von TradingView hat dieser Autor sein/ihr Script als Open-Source veröffentlicht. Auf diese Weise können nun auch andere Trader das Script rezensieren und die Funktionalität überprüfen. Vielen Dank an den Autor! Sie können das Script kostenlos verwenden, aber eine Wiederveröffentlichung des Codes unterliegt unseren Hausregeln.
Haftungsausschluss
Die Informationen und Veröffentlichungen sind nicht als Finanz-, Anlage-, Handels- oder andere Arten von Ratschlägen oder Empfehlungen gedacht, die von TradingView bereitgestellt oder gebilligt werden, und stellen diese nicht dar. Lesen Sie mehr in den Nutzungsbedingungen.